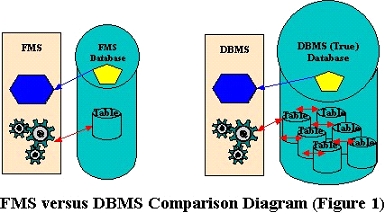
A Database Management System (DMS) is a combination of computer software, hardware, and information designed to electronically manipulate data via computer processing. Two types of database management systems are DBMS’s and FMS’s. In simple terms, a File Management System (FMS) is a Database Management System that allows access to single files or tables at a time. FMS’s accommodate flat files that have no relation to other files. The FMS was the predecessor for the Database Management System (DBMS), which allows access to multiple files or tables at a time (see Figure 1 below)
File Management Systems
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
1-Simpler to use
|
1-Typically does not support multi-user access
|
2-Less expensive·
|
2-Limited to smaller databases
|
3-Fits the needs of many small businesses and home users
|
3-Limited functionality (i.e. no support for complicated transactions, recovery, etc.)
|
4-Popular FMS’s are packaged along with the operating systems of personal computers (i.e. Microsoft Cardfile and Microsoft Works)
|
4-Decentralization of data
|
5-Good for database solutions for hand held devices such as Palm Pilot
|
5-Redundancy and Integrity issues
|
Typically, File Management Systems provide the following advantages and disadvantages:
The goals of a File Management System can be summarized as follows (Calleri, 2001):
- Data Management. An FMS should provide data management services to the application.
- Generality with respect to storage devices. The FMS data abstractions and access methods should remain unchanged irrespective of the devices involved in data storage.
- Validity. An FMS should guarantee that at any given moment the stored data reflect the operations performed on them.
- Protection. Illegal or potentially dangerous operations on the data should be controlled by the FMS.
- Concurrency. In multiprogramming systems, concurrent access to the data should be allowed with minimal differences.
- Performance. Compromise data access speed and data transfer rate with functionality.
From the point of view of an end user (or application) an FMS typically provides the following functionalities (Calleri, 2001):
- File creation, modification and deletion.
- Ownership of files and access control on the basis of ownership permissions.
- Facilities to structure data within files (predefined record formats, etc).
- Facilities for maintaining data redundancies against technical failure (back-ups, disk mirroring, etc.).
- Logical identification and structuring of the data, via file names and hierarchical directory structures.
Database Management Systems
Database Management Systems provide the following advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages
| Disadvantages |
Greater flexibility
|
Difficult to learn
|
Good for larger databases
|
Packaged separately from the operating system (i.e. Oracle, Microsoft Access, Lotus/IBM Approach, Borland Paradox, Claris FileMaker Pro)
|
Greater processing power
|
Slower processing speeds
|
Fits the needs of many medium to large-sized organizations
|
Requires skilled administrators
|
Storage for all relevant data
|
Expensive
|
Provides user views relevant to tasks performed
| |
Ensures data integrity by managing transactions (ACID test = atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability)
| |
Supports simultaneous access
| |
Enforces design criteria in relation to data format and structure
| |
Provides backup and recovery controls
| |
Advanced security
|
The goals of a Database Management System can be summarized as follows (Connelly, Begg, and Strachan, 1999, pps. 54 – 60):
- Data storage, retrieval, and update (while hiding the internal physical implementation details)
- A user-accessible catalog
- Transaction support
- Concurrency control services (multi-user update functionality)
- Recovery services (damaged database must be returned to a consistent state)
- Authorization services (security)
- Support for data communication Integrity services (i.e. constraints)
- Services to promote data independence
- Utility services (i.e. importing, monitoring, performance, record deletion, etc.)
The components to facilitate the goals of a DBMS may include the following:
- Query processor
- Data Manipulation Language preprocessor
- Database manager (software components to include authorization control, command processor, integrity checker, query optimizer, transaction manager, scheduler, recovery manager, and buffer manager)
- Data Definition Language compiler
- File manager
I like that kind of information, not only i like that post all peoples like that post, because of all given information was very excellent.
ReplyDeleteDocument Management Software
Electronic Document Management System
Cloud Document Management System
Document Management System
Electronic Document Management Software
Really very great information for that post, am amazed and then more new information are get after refer that post. I like that post.
ReplyDeleteDocument Management Software India
Document Management Software Chennai
Document Management Software
Electronic Document Management System